Author: Zoey
In contemporary medicine, blood test results are used in 80% of diagnoses. Blood tests can be used to identify a wide range of medical conditions, including blood abnormalities, bacterial infections, viruses, and even some forms of cancer. However, if the blood is contaminated during the draw, these critically vital tests are worthless, which is why a highly trained and efficient phlebotomist is such an essential element of the procedure. The following are some attentions and procedures of blood draw.
During blood collection and treatment of blood specimens, gloves, masks, and other personal protective equipment shall be worn to avoid splashing and leakage of blood specimens and exposure to potential pathogens.
Use anti-reflux needles for blood collection and all used blood collection "sharps" (such as blood collection needles, syringe needles, etc.) should be disposed of in the designated sharps containers.
All biologically hazardous specimens and blood collection "sharps" (e.g., blood collection needles, syringe needles, etc.) should be handled in accordance with product regulations and procedures, and improper handling may result in biological risks (e.g., viral hepatitis, HIV, or other infectious disease infection if accidentally pricked).
If the blood sample is collected by intravenous injection, it should be confirmed that the solution in the pipe has been completely removed before blood collection, so as to avoid erroneous experimental results due to the contamination of the solution in the pipe.
Too much or too little blood collection will lead to an incorrect ratio of additives to blood, which may lead to incorrect analysis results.
When using blood collection tubes, you should carefully identify the altitude zone for which the tube is intended. Mixing tubes from different altitudes can result in insufficient or excessive blood draws.
Prolonged open-cap storage of blood collection tubes can lead to evaporation of water, resulting in incorrect analytical results. Therefore, please take care to seal the cap promptly.
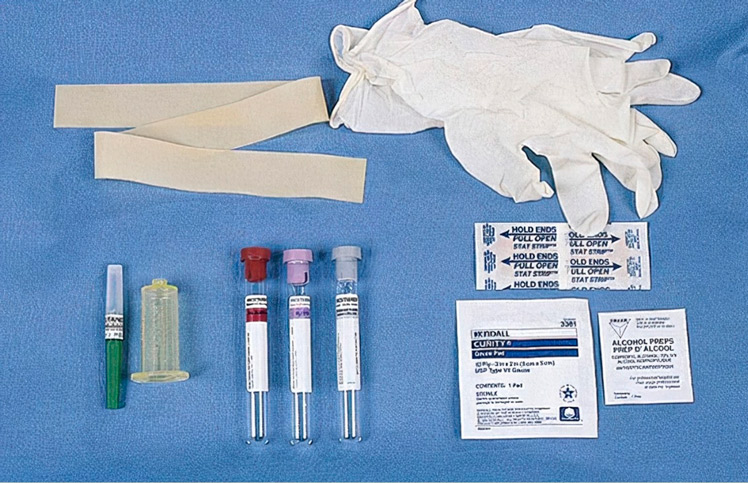
Preparation before blood drawing: wear masks, gloves, and other necessary personal protective equipment.
Prepare sterile alcohol, dry sterile swabs, pulse strips, and blood collection tubes and needles for blood collection.
Reconfirm blood collection tube size, aspirate volume, and additives, and mark the label with patient information if necessary.
Prevention of backflow: Most vacuum blood collection tubes contain chemical additives, and the following precautions are necessary to prevent adverse reactions in patients caused by backflow:
It is recommended to use a blood collection needle with an anti-backflow device.
Orienting the patient's arm in an inferior position.
Keep the tube cap facing upward while collecting blood.
Release the pulse band as soon as the blood starts to enter the blood collection tube.
Blood collection with the butterfly needle:
(1) Tear open the small packaging bag of the blood collection needle, take out the blood collection needle and remove the plastic protective cover at the end of the venipuncture needle.
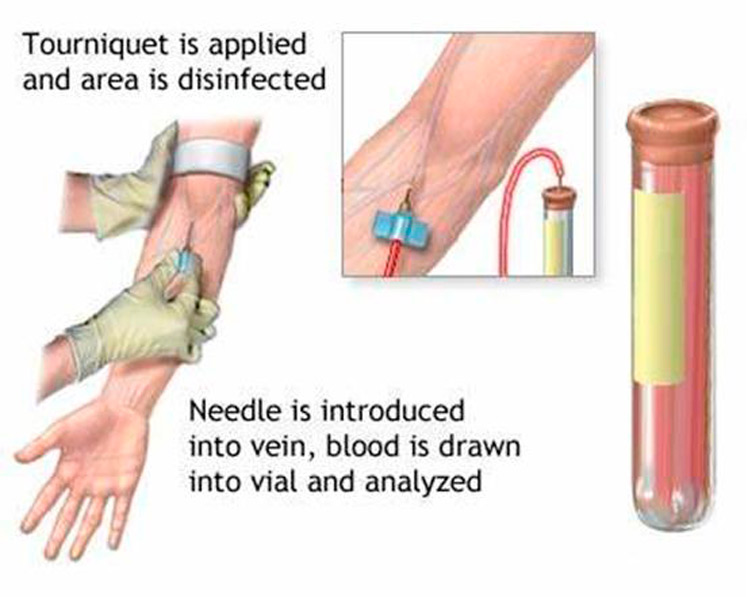
(2) Fasten the pulse pressure belt for the patient and disinfect the puncture site (do not touch the area with your hands after disinfection).
(3) The puncture is performed after the sterile alcohol has evaporated naturally, and a successful puncture is indicated by the return of blood.
(4) Pierce the tube plug puncture needle vertically through the rubber plug of the blood collection tube, and release the pulse pressure band after seeing the blood flow into the tube.
(5) When the first tube has been collected and the blood flow has stopped, pull the tube out. When multiple tubes need to be collected, continue collecting in the correct order of blood draw.
(6) Immediately after blood collection, shake it gently by reversing 180 degrees according to the recommended number of times to fully mix the additive and blood sample.
(7) When the blood stops flowing into the last tube, the needle should be immediately removed from the vein. Press the puncture site with a sterilized cotton swab and hold it for more than 10 minutes until the blood stops flowing.
(8) Dispose of used blood collection needles in the sharps containers and prohibit reuse.
(9) Send samples for inspection in time.
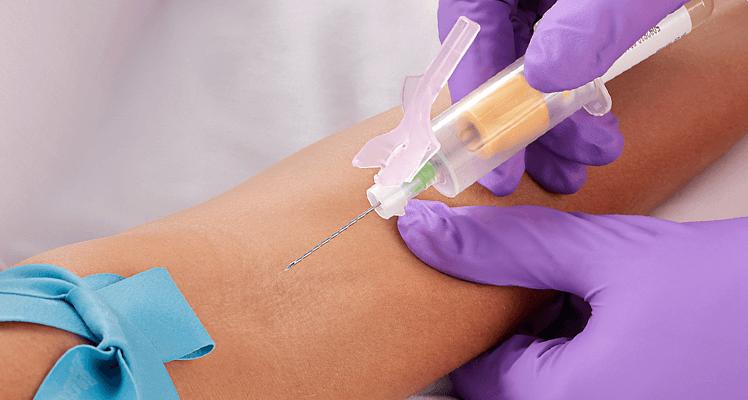
Blood collection with the straight needle:
(1) Unscrew the protective sleeve at the puncture needle end of the tube plug.
(2) Screw the plug puncture needle into the needle holder and tighten it.
(3) Fasten the pulse pressure belt for the patient and disinfect the puncture site (do not touch the area with hands after disinfection).
(4) Let the patient's arm hang down, remove the venipuncture needle sheath, and let the sterile alcohol evaporate naturally before performing the puncture.
(5) Hold the end of the tube with your thumb and push it into the needle holder so that the blood collection needle pierces the rubber plug (be careful to keep the needle pierced equally from the center of the plug as much as possible) and release the pressure band when you see blood flowing into the tube.
(6) When the first tube has been collected and the blood flow has stopped, pull the tube out of the needle holder.
(7) Immediately after blood collection, shake it gently by reversing 180 degrees according to the recommended number of times to fully mix the additive and blood sample.
(8) When the blood stops flowing into the last tube, the needle should be immediately removed from the vein. Press the puncture site with a sterilized cotton swab and hold it for more than 10 minutes until the blood stops flowing.
(9) Dispose of used blood collection needles in the sharps containers and prohibit reuse.
(10) Send samples for inspection in time.
Reference:
https://nurse.org/articles/how-nurses-professionally-draw-blood/
https://pathlabs.ufl.edu/client-services/specimen-shipping/blood-collection-process-venipuncture/
https://americanmedtech.org/files/STEP_Online_articles/270.pdf
Gongdong Medical is an experienced high-end OEM medical blood tube factory, supplier, and manufacturer in China. Welcome to contact.