

Views: 22 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-12 Origin: Site








Blood collection tubes are crucial in medical diagnostics and research, helping to separate and store specific components of blood for various tests. Among these tubes, the SST tube and Red Top tube are two of the most commonly used. While both are used for serum collection, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. In this article, we will compare the SST tube and the Red Top tube, examining their differences, advantages, and specific uses in laboratory settings.
The SST tube, also known as a Serum Separator Tube, is a blood collection tube designed to separate serum from blood after centrifugation. The SST tube is typically made of glass or plastic, with a special gel separator inside. This gel is located between the serum and cellular components of the blood, and it plays a key role in ensuring that the serum is separated quickly and efficiently.
The SST tube is primarily used for tests that require serum rather than plasma, as serum is the liquid portion of blood after it has clotted and separated from the blood cells.
After blood is collected into an SST tube, it is placed in a centrifuge where it is spun at high speeds. The centrifugal force causes the heavier blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets) to settle at the bottom of the tube. The gel separator forms a physical barrier between the serum and the cellular components, making it easier to isolate the serum.
This process allows medical professionals to collect a pure serum sample, free from cellular debris, which is essential for accurate diagnostic testing.
SST tubes are used in a variety of diagnostic tests, including:
Blood Chemistry Panels: Used to measure glucose, electrolytes, liver enzymes, kidney function markers, and other important blood parameters.
Hormonal Tests: To measure levels of hormones such as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), cortisol, and others.
Liver and Kidney Function Tests: Measuring liver enzymes, bilirubin, kidney markers like creatinine and BUN (blood urea nitrogen).
Infectious Disease Testing: SST tubes are used to collect serum samples for testing antibodies or antigens related to various infections.
The gel separator in SST tubes ensures that serum is collected without contamination, speeding up the process and ensuring the sample’s integrity.
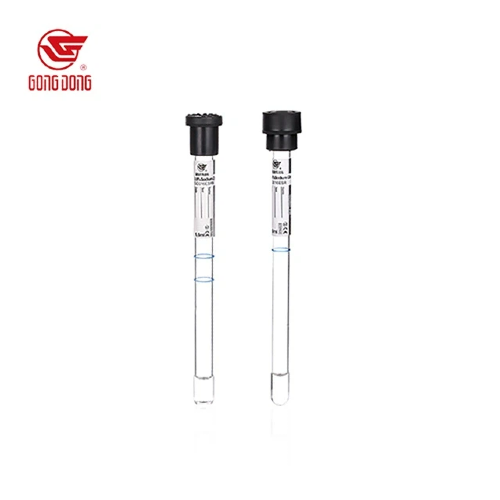


The Red Top tube is a plain blood collection tube with no additives or gel separators. This simplicity allows the blood to clot naturally. Like the SST tube, it can be made of either glass or plastic. However, unlike the SST tube, it does not contain a gel separator and relies solely on the blood’s ability to clot on its own.
When blood is collected into a Red Top tube, it must be allowed to clot naturally before being processed. The clotting process takes time, typically around 30 minutes at room temperature, during which the blood will form a clot at the bottom of the tube. After this clotting period, the tube is centrifuged to separate the serum from the clot.
Without a gel separator, this method requires additional time and careful handling, but it is effective for collecting pure serum for specific tests.
Red Top tubes are commonly used for:
Serum Collection: Ideal for tests that require pure serum, including certain immunoassays and antibody tests.
Specialized Blood Chemistry Tests: Some blood tests, such as those for certain hormones or markers, may require serum from a Red Top tube.
Research Applications: The Red Top tube is often used in research studies, where the serum must be free from additives or when specific clotting conditions are required.
Understanding the core differences between the SST tube and the Red Top tube can help laboratory professionals choose the correct tube for their tests.
Feature | SST Tube | Red Top Tube |
Additives | Contains a gel separator for faster serum separation | No additives, plain tube for natural clotting |
Gel Separator | Yes, a gel separator forms a barrier between serum and cells | No gel separator |
Material | Can be made of glass or plastic | Can be made of glass or plastic |
SST Tube: Contains a gel separator that forms a physical barrier between the serum and blood cells, allowing for faster serum separation.
Red Top Tube: No additives, allowing the blood to clot naturally before serum is separated. This requires additional time compared to the SST tube.
The processing time for serum separation differs significantly between the two tubes:
SST Tube: Due to the gel separator, serum separation is quicker. The tube typically requires about 10-15 minutes of centrifugation.
Red Top Tube: Serum separation in a Red Top tube requires a longer time for clotting (30 minutes) before the centrifugation process. The overall processing time is therefore longer than for the SST tube.
Test Type | SST Tube | Red Top Tube |
Blood Chemistry Tests | Yes, ideal for routine testing | Yes, but takes longer for serum separation |
Hormonal Tests | Yes, widely used for hormone assays | Yes, but slower serum separation |
Infectious Disease Testing | Yes, commonly used for serological tests | Less common, used in specialized or research settings |
The SST tube is used more widely in clinical settings, especially when a quick turnaround time is required for tests like chemistry panels or hormonal assays. The Red Top tube, on the other hand, is often used in specialized research or when serum must be collected without any additives or gel.
The SST tube has several key advantages that make it a preferred choice in many clinical and research laboratories.
The presence of the gel separator allows for faster separation of serum from the blood components. This is especially important in high-volume laboratories where quick results are needed. SST tubes typically require only 10-15 minutes of centrifugation, allowing for a quicker turnaround time for diagnostic tests.
Because the SST tube’s gel separator automatically isolates the serum, there is less handling required. This reduces the risk of contamination or mishandling of the sample, ensuring that the serum collected is as pure as possible.
Given the efficiency and speed of the SST tube, it is ideal for high-throughput testing. Laboratories that need to process large numbers of samples quickly, such as those performing routine blood chemistry panels or hormonal tests, benefit from the SST tube’s fast processing time.
The gel separator in SST tubes ensures a consistent and reliable serum separation every time, helping labs achieve more accurate and reproducible test results.
The Red Top tube also offers several advantages, especially in certain testing scenarios.
The Red Top tube does not contain any additives or separators, which makes it ideal for tests that require untreated serum. This is particularly important in certain antibody tests or research applications, where pure serum without any added chemicals is required.
Red Top tubes are typically less expensive than SST tubes. For laboratories with budget constraints or for tests that do not require fast serum separation, the Red Top tube offers a more cost-effective option without compromising the quality of the results.
The natural clotting process in the Red Top tube is beneficial for certain immunoassays or tests where the serum must be collected after the blood clots naturally. This feature makes the Red Top tube versatile in specific diagnostic and research environments.
The simplicity of the Red Top tube makes it suitable for a wide variety of tests and applications, including those where additives could interfere with the results. It is often used in research settings or for specialized tests where serum purity is crucial.
Use an SST tube when:
Quick serum separation is needed for routine diagnostic tests like chemistry panels and hormonal assays.
A gel separator is required for efficient serum collection.
High-volume testing is being performed, where speed and consistency are essential.
Use a Red Top tube when:
Natural clotting is required for specific tests or research applications.
You need untreated serum for tests like immunoassays or antibody testing.
A cost-effective option is preferred for tests that do not require rapid serum separation.
Both the SST tube and Red Top tube play vital roles in clinical diagnostics and research, each offering unique benefits based on the specific requirements of the test. The SST tube is perfect for situations where quick serum separation is needed, ensuring faster results for high-volume tests. In contrast, the Red Top tube is ideal for cases where natural clotting is required or when tests demand a plain, additive-free serum.
Choosing the appropriate tube for each test is essential for obtaining accurate and timely results. By understanding the key differences between these two tubes, laboratories can make more informed decisions and streamline their diagnostic processes.
At Zhejiang Gongdong® Medical Technology Co., Ltd., we specialize in providing high-quality blood collection tubes, including both SST and Red Top tubes. Our expertise in manufacturing and supplying reliable medical consumables ensures that you have the right tools for your laboratory's needs. We invite you to reach out to us for more information or to discuss how we can support your diagnostic and research requirements. Let us help you achieve the best results with our trusted products and services.
The main difference is that the SST tube contains a gel separator, which speeds up serum separation, while the Red Top tube is a plain tube that requires natural clotting before serum separation.
While both tubes collect serum, the SST tube is preferred for tests requiring quick serum separation. The Red Top tube is better for tests where natural clotting is necessary.
The gel separator in the SST tube facilitates faster serum separation, while the Red Top tube relies on clotting, which takes additional time.
The SST tube is typically better for blood chemistry tests as it provides faster serum separation and quicker results.
Red Top tubes are used for tests that require untreated serum or when natural clotting is preferred, such as specific immunoassays and research studies.